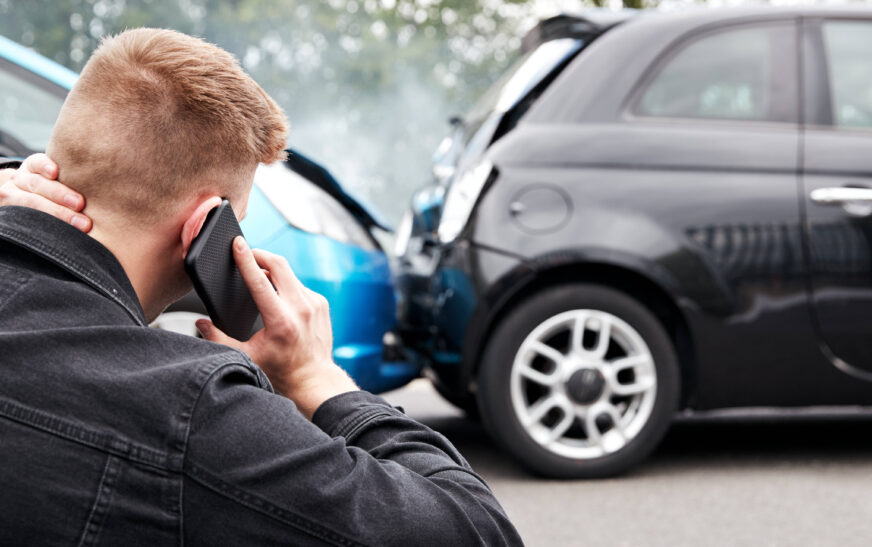
Understanding Car Accident Liability
Car accidents are an unfortunate reality of modern life, causing significant distress, injuries, and financial burdens. Understanding car accident liability is crucial in determining who is responsible for the damages and injuries sustained in a crash. Liability refers to one party’s legal responsibility for harm caused to another. In the context of car accidents, this usually means determining who was at fault and, therefore, who should compensate the injured parties. This article will delve into the intricacies of car accident liability, offering a comprehensive guide to help you understand your rights and the legal processes involved.
Types of Car Accidents and Their Impact on Liability
The type of car accident significantly influences the determination of liability. Various factors, such as the nature of the collision, the location of the impact, and the behavior of the drivers involved, play a role in assessing fault. Here are some common types of car accidents and how they impact liability:
Rear-End Collisions
Rear-end collisions occur when one vehicle crashes into the back of another. In most cases, the driver of the rear vehicle is presumed to be at fault for failing to maintain a safe distance or failing to stop in time. However, there are exceptions, such as when the front vehicle makes a sudden and unexpected stop without a valid reason.
Side-Impact Collisions (T-Bone)
Side-impact collisions, or T-bone accidents, happen when the front of one vehicle crashes into the side of another. These accidents often occur at intersections and can be particularly dangerous. Liability in T-bone collisions is typically determined by examining which driver had the right of way. Traffic signals, stop signs, and witness statements can help establish fault.
Head-On Collisions
Head-on collisions are among the most severe types of accidents, often resulting in serious injuries or fatalities. These accidents usually occur when one vehicle crosses the center line or drives the wrong way on a one-way street. Determining liability in head-on collisions involves investigating whether one of the drivers was impaired, distracted, or engaging in reckless behavior.
Multi-Vehicle Pile-Ups
Multi-vehicle pile-ups involve several cars and can be complex in terms of liability. In these situations, multiple drivers may share responsibility for the accident. Investigators will examine the sequence of events, the speed of the vehicles, and other contributing factors to determine the extent of each driver’s fault.
Determining Fault in a Car Accident
Determining fault in a car accident is a critical aspect of establishing liability. Various methods and evidence are used to ascertain who was responsible for the crash. Here are some key factors that help determine fault:
Police Reports
Police reports are essential in determining fault as they provide an official account of the accident. Officers at the scene document details such as the location, time, weather conditions, and statements from drivers and witnesses. These reports often include the officer’s opinion on who was at fault, which can be influential in insurance claims and legal proceedings.
Eyewitness Testimonies
Eyewitnesses can provide valuable insights into how the accident occurred. Their statements can corroborate or contradict the accounts given by the drivers involved. Independent witnesses, those not related to either driver, are especially credible and can significantly impact the determination of fault.
Traffic Laws
Traffic laws and regulations are fundamental in determining fault. Violations of these laws, such as running a red light, speeding, or failing to yield, can establish negligence on the part of a driver. The specific laws applicable to the accident’s location are considered to determine which driver breached their duty of care.
Surveillance Footage
In today’s digital age, surveillance cameras are prevalent and can capture car accidents as they happen. Footage from traffic cameras, nearby businesses, or dashcams can provide clear evidence of the events leading up to the accident and help determine fault.
The Role of Negligence in Car Accident Liability
Negligence is a cornerstone in car accident liability. It refers to a driver’s failure to exercise reasonable care, resulting in harm to another person. To establish negligence, the following elements must be proven:
Duty of Care
All drivers have a duty of care to operate their vehicles safely and follow traffic laws. This duty extends to other drivers, passengers, pedestrians, and anyone who might be affected by their actions on the road.
Breach of Duty
A breach of duty occurs when a driver fails to meet the standard of care expected of them. This could involve actions such as speeding, texting while driving, or disregarding traffic signals. The breach of duty is a critical element in proving negligence.
Causation
Causation links the breach of duty to the accident and resulting injuries. It must be shown that the driver’s negligence directly caused the accident and that the injuries sustained were a foreseeable result of their actions.
Damages
Finally, damages refer to the losses suffered by the injured party, including medical expenses, lost wages, pain and suffering, and property damage. These damages must be directly linked to the accident and the negligent actions of the responsible driver.
Comparative and Contributory Negligence
In some car accident cases, fault is not entirely placed on one party. Comparative and contributory negligence are legal doctrines that address situations where multiple parties share responsibility for an accident.
Comparative Negligence
Comparative negligence allocates fault among the parties involved in an accident based on their respective contributions to the incident. There are two types of comparative negligence:
- Pure Comparative Negligence: Under pure comparative negligence, each party is assigned a percentage of fault, and they can recover damages reduced by their degree of fault. For example, if a driver is found 30% at fault and the other driver 70%, the first driver can still recover 70% of their damages.
- Modified Comparative Negligence: In modified comparative negligence states, a party can only recover damages if their fault is below a certain threshold, typically 50%. If a driver is found to be more than 50% at fault, they cannot recover any damages.
Contributory Negligence
Contributory negligence is a stricter doctrine where any fault on the part of the injured party bars them from recovering any damages. Even if the injured party is found to be only 1% at fault, they cannot recover compensation. This doctrine is less common and is considered harsh compared to comparative negligence.
Conclusion
Understanding car accident liability is essential for anyone involved in a crash. Determining who is responsible for injuries and damages requires a thorough investigation of the accident, including police reports, eyewitness testimonies, and adherence to traffic laws. Negligence plays a crucial role in establishing fault, and doctrines like comparative and contributory negligence further complicate liability in multi-party accidents. If you are involved in a car accident, seeking the assistance of a knowledgeable Los Angeles car accident attorney is crucial. They can help navigate the complexities of car accident liability and ensure you receive the compensation you deserve.
For more information or to discuss your case with an experienced Los Angeles car accident lawyer, contact our team at the Law Offices of Howard Kornberg. We specialize in personal injury cases and have a proven track record of helping clients in Los Angeles secure fair compensation for their injuries.
Feel free to submit more guest posts through Links Building Servcies - Best Prices. Buy Author Account / 1$ Guest Post Here




![How to transfer money from Robinhood to bank account? [Steps]](https://hollywoodrag.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Banking-Across-Europe.jpg)