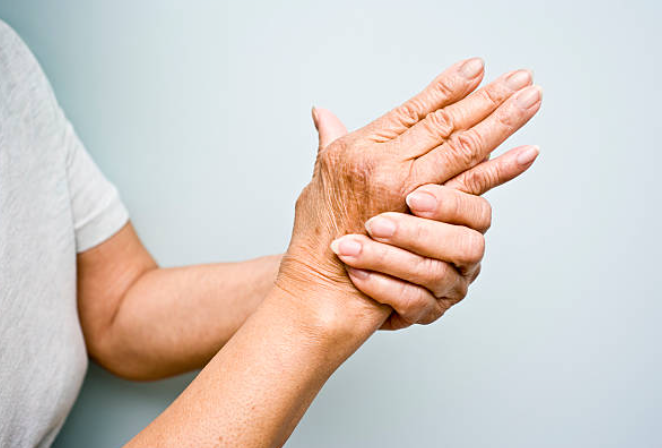
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and potential joint damage. Recognizing the symptoms of RA early on is crucial for effective management and treatment. This comprehensive guide explores the common symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and their impact on daily life.
More Details : What Is The Rheumatoid Arthritis
1. Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis
1.1. What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, the lining of the joints. This results in inflammation, swelling, and pain, which can lead to joint damage over time. RA can also affect other parts of the body, including the skin, eyes, and organs.
1.2. How RA Differs from Osteoarthritis
Unlike osteoarthritis, which is primarily caused by wear and tear on the joints, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition. RA typically affects multiple joints symmetrically, whereas osteoarthritis often affects individual joints.
2. Common Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
2.1. Joint Pain and Tenderness
Joint pain is one of the hallmark symptoms of RA. It often affects the small joints of the hands and feet but can also involve larger joints such as the knees, shoulders, and hips. The pain is usually persistent and can vary in intensity from mild to severe.
2.2. Joint Swelling
Inflammation caused by RA leads to swelling in the affected joints. This swelling is often accompanied by redness and warmth around the joints. The swelling can make it difficult to move the affected joints and perform everyday activities.
2.3. Morning Stiffness
A common symptom of RA is morning stiffness, where joints feel stiff and difficult to move after waking up. This stiffness can last for several hours and may improve as the day progresses. Morning stiffness is often used as an indicator of RA in diagnosis.
2.4. Fatigue
Fatigue is a common and debilitating symptom of RA. Individuals with RA often experience an overwhelming sense of tiredness, which is not necessarily related to physical activity. This fatigue can affect daily functioning and quality of life.
2.5. Loss of Joint Function
As RA progresses, it can lead to a loss of joint function. This loss can be due to joint damage, pain, and inflammation. Individuals may find it increasingly difficult to perform tasks such as gripping objects, walking, or climbing stairs.
2.6. Fever and Weight Loss
Some people with RA may experience low-grade fevers and unintended weight loss. These systemic symptoms are less common but can indicate more severe disease activity or complications.
2.7. Rheumatoid Nodules
Rheumatoid nodules are firm, painless lumps that can develop under the skin, usually near the elbows, hands, or feet. These nodules are a result of chronic inflammation and are seen in some people with RA.
3. Systemic Effects of Rheumatoid Arthritis
3.1. Impact on Other Organs
In addition to joint symptoms, RA can affect other organs and systems in the body. This may include the eyes (causing dryness or inflammation), lungs (leading to respiratory issues), and cardiovascular system (increasing the risk of heart disease).
3.2. Psychological Effects
The chronic pain and disability associated with RA can lead to psychological effects such as depression and anxiety. Managing these psychological aspects is an essential part of comprehensive RA care.
4. Diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis
4.1. Clinical Evaluation
Diagnosis of RA typically involves a clinical evaluation by a healthcare provider, including a review of symptoms, physical examination, and medical history. Early diagnosis is critical for effective treatment and management.
4.2. Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests such as rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) tests can help in diagnosing RA. Elevated levels of these antibodies are often associated with the disease.
4.3. Imaging Studies
Imaging studies, such as X-rays or ultrasounds, can assess the extent of joint damage and inflammation. These studies help in monitoring disease progression and guiding treatment decisions.
5. Management and Treatment
5.1. Medications
Treatment for RA often includes medications to reduce inflammation, manage pain, and slow disease progression. Common medications include disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologics.
5.2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help improve joint function, strengthen muscles around the joints, and enhance overall mobility. Customized exercise programs can be beneficial in managing RA symptoms.
5.3. Lifestyle Adjustments
Making lifestyle adjustments such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help in managing RA symptoms and improving overall well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis is crucial for early detection and effective management of the condition. By recognizing common symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, morning stiffness, and fatigue, individuals can seek timely medical intervention and improve their quality of life. Comprehensive treatment plans, including medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, are essential for managing RA and reducing its impact on daily life.
Feel free to submit more guest posts through Links Building Servcies - Best Prices. Buy Author Account / 1$ Guest Post Here